CS231n-Unsupervised Learning and Generative Models
Last updated on December 22, 2024 am
Unsupervised Learning and Generative Models
Unsupervised Learning
Supervised Learning
- Data: (x,y) x is data, y is label
- Goal: Learn a function to map s→y
- Examples: Classification, regression, object detection, semantic segmentation, image caption, etc.
Unsupervised Learning
- Data: x,just data, no labels!
- Goal: Learn some underlying hidden structure of some data
- Examples: Clustering, Dimensionality reduction(principal Component Analysis),feature learning, density estimation,etc.
Generative Models
Given training data, geneerate new samples from same distribution.
- Explicit density
- Tractable demsity
- Fully Visible Belief Nets(Change of variables models(nonlinear ICA))
- NADE
- MADE
- PixelRNN/CNN
- Approximate density
- Variational: Variational Autoencoders
- Markov Chain: Boltzmann Machine
- Fully Visible Belief Nets(Change of variables models(nonlinear ICA))
- Tractable demsity
- Implicit density
- Direct(GAN)
- Markov Chain(GSN)
PixelRNN and PixelCNN
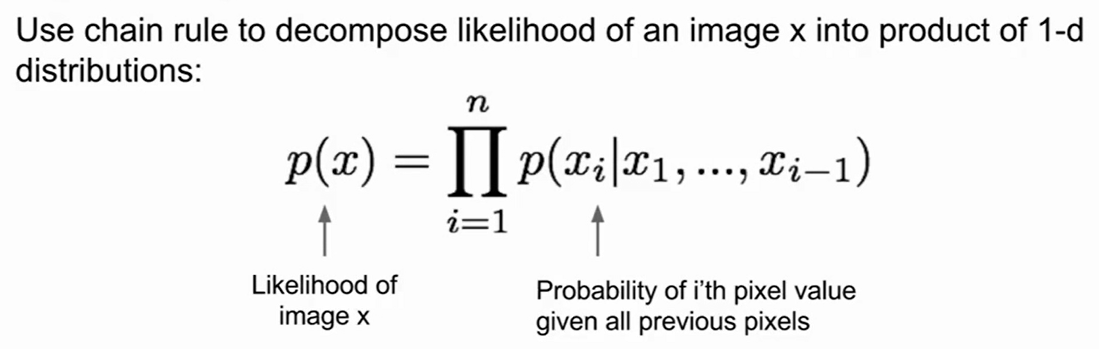
- use neural network to express this comlex distribution!
- PixelCNN与semantic Segmentation的区别:一个是直接使用原始图片的像素值,一个是使用人工标注的语义分割图片
Variational Autoencoders(VAE)
这里视频讲的不是很清楚,推荐苏老师的博客

在讨论VAE之前,我们先来看一看Autoencoders
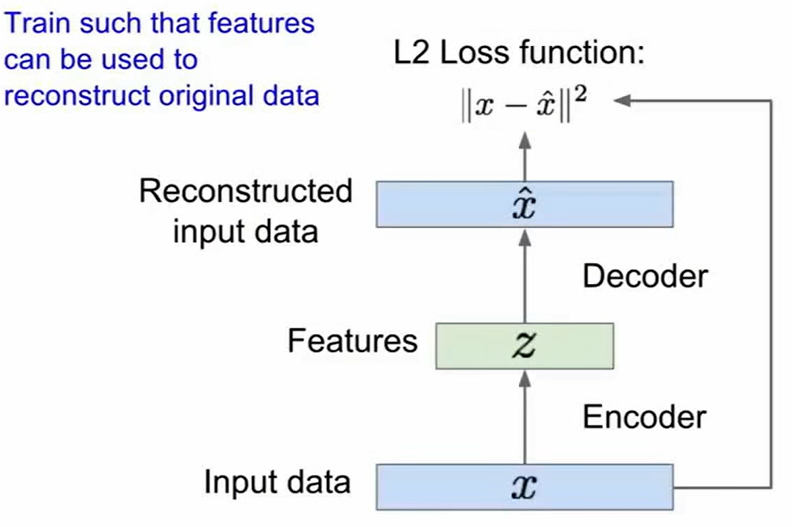
在学习之前先使用Autoencoders,可以减少features的数量,从而减少过拟合的风险
AE可以起到降维的作用,但是它不能产生新的采样以达到增加样本的作用
- 在样本量不足的场景当中,我们想要增加样本量以达到更好的效果。如果能够根据一批一批数据样本${X_1,…,X_n}$直接找到$X$的分布$p(X)$,那我直接根据$p(X)$来采样就可以了。但是这是不能实现的。
- 于是我们曲线救国,把AE中的向量z(确定的)改为一个正态分布(不确定的)这样我们就把有限的数据样本扩展到无穷维了(应为正态分布里面可以随便采样)(使用正态分布是启发式的)
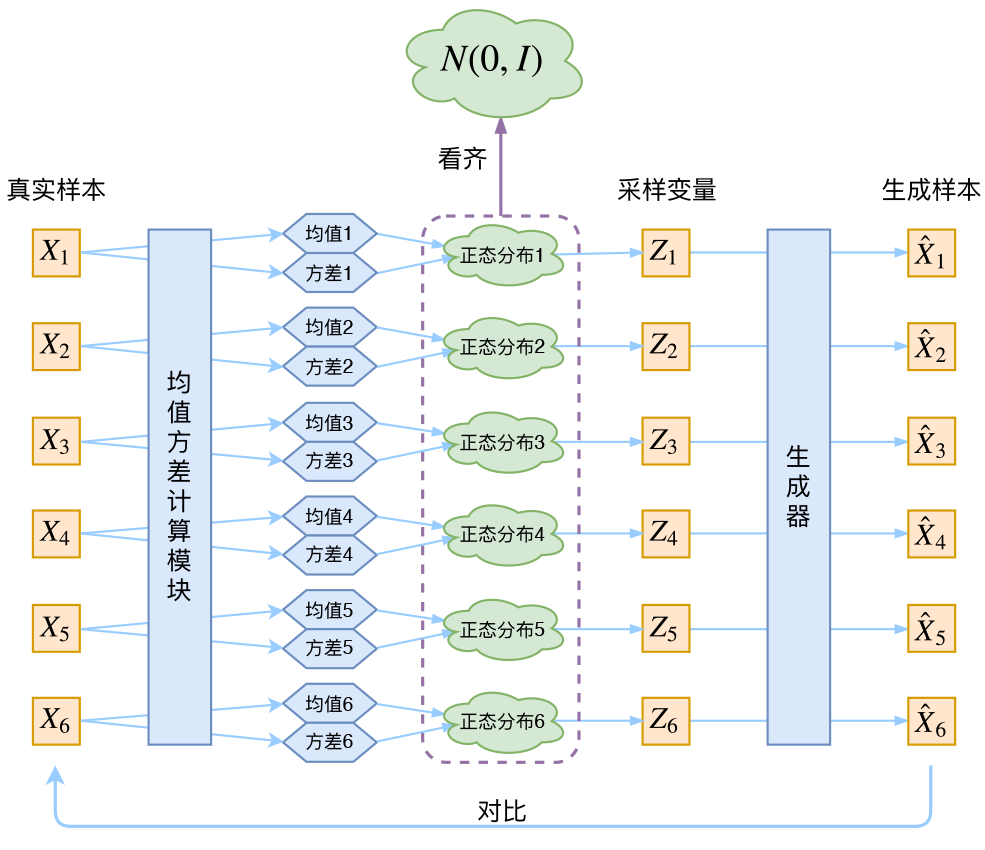
其中均值方差计算模块与生成器模块都是由网络实现的(什么不好算就交给网络,这是神经网络时代的哲学)
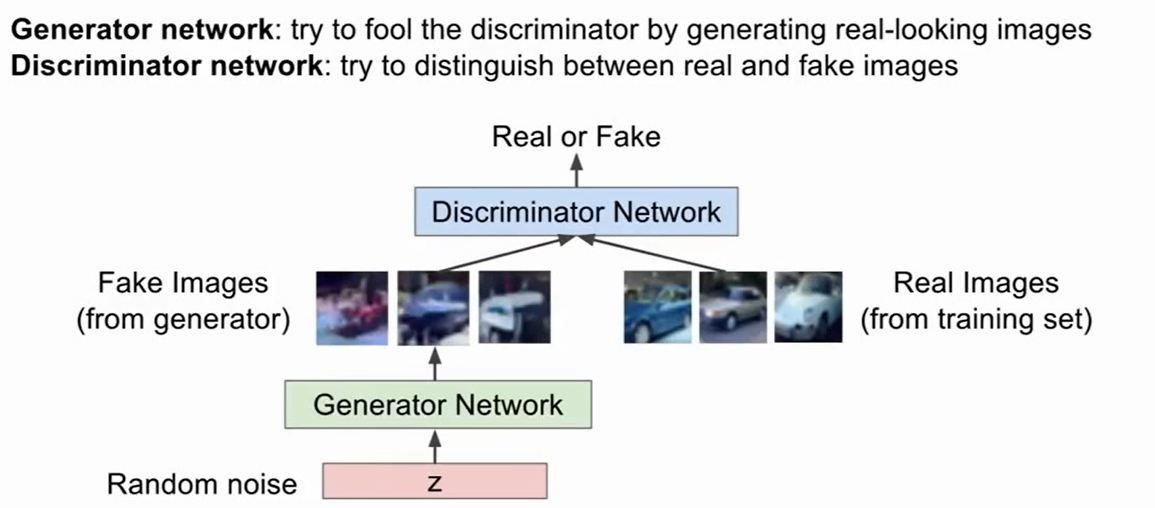
Generative Adversarial Networks(GAN)
当样本的分布过于复杂之时,我们可以放弃考虑样本分布,转而使用一个博弈的思想,一个Generator network,和一个Discriminator network,生成网络尝试去欺骗过判别网络,判别网络尝试去区分出真与假的照片。
我们最小化下面这个函数
$$
\min_{\theta_g}\max_{\theta_g}[E_{x-p_{data}}\log D_{\theta_d}(x)+E_{z-p(z)}\log (1-D_{\theta_d}(G_{\theta_g}(z)))]
$$
步骤:
Gradient Ascent on discriminator
$$
\max_{\theta_g}[E_{x-p_{data}}\log D_{\theta_d}(x)+E_{z-p(z)}\log (1-D_{\theta_d}(G_{\theta_g}(z)))]
$$Gradient descent on generator
$$
\min_{\theta_g}E_{z-p(z)}\log (1-D_{\theta_d}(G_{\theta_g}(z)))
$$
但是对于生成器的目标函数,注意到它在生成质量不好时梯度较小,生成质量较小时梯度较大,这是我们不希望的,网络收敛速度很慢,于是我们转而最大化下面这个函数:
$$
\max_{\theta_g}E_{z-p(z)}\log D_{\theta_d}(G_{\theta_g}(z))
$$