lec04-C基础3
约 615 个字 89 行代码 5 张图片 预计阅读时间 4 分钟 共被读过 次
内存区域¶
- 栈、旗、静态数据、代码区
动态内存管理¶
malloc,calloc,realloc,free...
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
char source[] = "Hello, World!";
// 计算源字符串的长度(不包括 '\0')
size_t length = strlen(source);
// 动态分配内存,+1 是为了存储 '\0'
char *destination = malloc(sizeof(char) * (length + 1));
if (destination == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed!\n");
return 1;
}
// 使用 strcpy 复制字符串
strcpy(destination, source); // 不会检查destination的长度,所以必须确保有足够的长度
// strncpy(destination, source, length + 1)
printf("Source: %s\n", source);
printf("Destination: %s\n", destination);
// 释放动态分配的内存
free(destination);
return 0;
}
输入输出的用法¶
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int c;
printf("请输入一个字符: ");
c = getchar(); // 从标准输入读取一个字符
printf("你输入的字符是: %c\n", c);
FILE *file = fopen("example.txt", "r");
if (file) {
c = getc(file); // 从文件读取一个字符
printf("文件中的第一个字符是: %c\n", c);
fclose(file);
}
char buffer[100];
printf("请输入一行文本: ");
fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), stdin); // 从标准输入读取一行文本
printf("你输入的文本是: %s", buffer)
FILE *file = fopen("example.txt", "r");
if (file) {
fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), file); // 从文件读取一行文本
printf("文件中的第一行是: %s", buffer);
fclose(file);
}
int i = 42;
float f = 3.14;
printf("整数: %d, 浮点数: %.2f\n", i, f); // 输出到标准输出
FILE *file = fopen("output.txt", "w");
if (file) {
fprintf(file, "整数: %d, 浮点数: %.2f\n", i, f); // 输出到文件
fclose(file);
}
int i;
float f;
printf("请输入一个整数和一个浮点数: ");
scanf("%d %f", &i, &f); // 从标准输入读取整数和浮点数
printf("你输入的整数是: %d, 浮点数是: %.2f\n", i, f);
FILE *file = fopen("input.txt", "r");
if (file) {
fscanf(file, "%d %f", &i, &f); // 从文件读取整数和浮点数
printf("文件中的整数是: %d, 浮点数是: %.2f\n", i, f);
fclose(file);
}
char buffer[100];
int i = 42;
float f = 3.14;
sprintf(buffer, "整数: %d, 浮点数: %.2f", i, f); // 将格式化字符串写入buffer
printf("sprintf的结果: %s\n", buffer);
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "整数: %d, 浮点数: %.2f", i, f); // 安全地写入buffer
printf("snprintf的结果: %s\n", buffer);
return 0;
}
函数指针¶
- You have a function definition"
- charfoo(chara, int b){ …}
- Can create a pointer of that type…"
- char(f)(char*, int);
- Declares f as a function taking a char and an int and returning a char"
- char(f)(char*, int);
- Can assign to it"
- f=&foo
- Create a reference to function foo
- f=&foo
- And can then call it..."
- printf(“%s\n”,(*f)(“cat”, 3))
程序安全¶
- 使用工具检测问题:
vlagfind
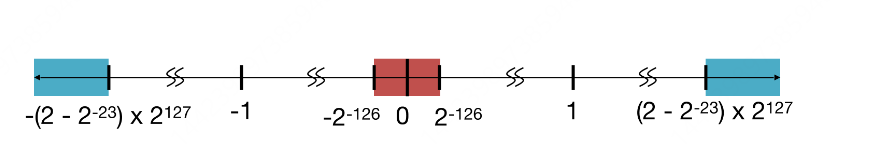
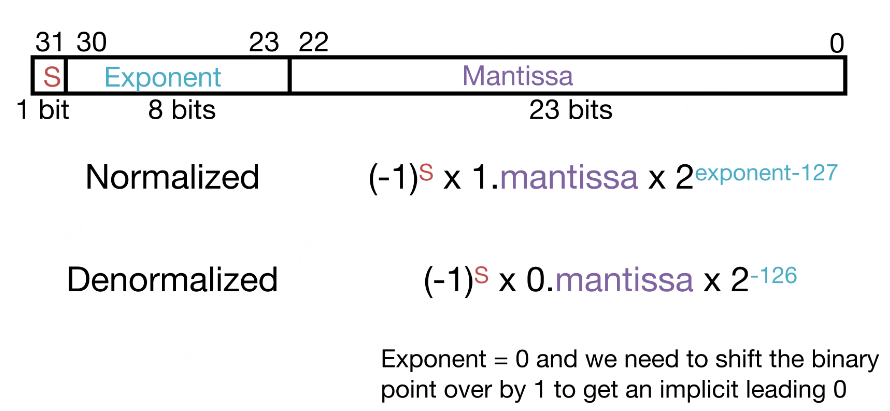
Float¶
| Type | Exponent | Mantissa |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Number | 1-254 | Anything |
| Zero | All zeros | All zeros |
| Infinity | All ones(255) | All zeros |
| NaN | All ones(255) | Nonzero |
| Denorm | All zeros | Nonzero |
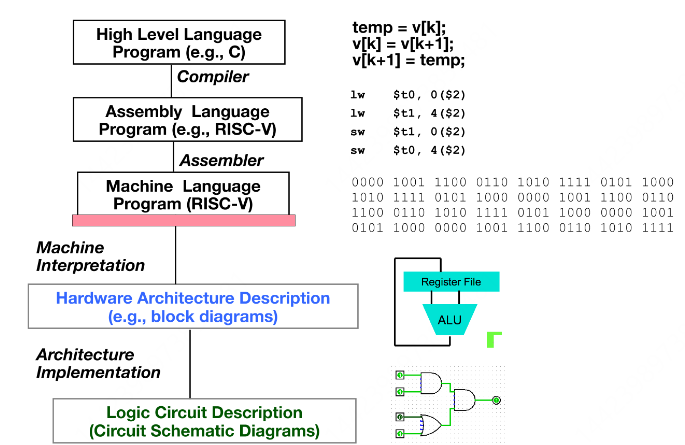
Instruction Set Architecture(ISA)
- Examples: ARM, Intel x86, MIPS, RISC-V, IBM/Motorola PowerPC(old Mac)
RISCV Instructions:
算术运算指令¶
add x1, x2, x3# x1 = x2 + x3sub x1, x2, x3# x1 = x2 - x3addi x1, x2, 10# x1 = x2 + 10,立即数加法,将寄存器x2的值加上10 后存到x1
逻辑运算指令¶
and x1, x2, x3# x1 = x2 & x3,按位与操作or x1, x2, x3# x1 = x2 | x3,按位或操作xor x1, x2, x3# x1 = x2 ^ x3,按位异或操作andi x1, x2, 0xFF# x1 = x2 & 0xFF,将寄存器x2的值与立即数0xFF按位与后存到x1
移位运算指令¶
sll x1, x2, x3# x1 = x2 << x3,逻辑左移,将寄存器x2的值左移 x3位后存到x1slli x1, x2, c
srl x1, x2, x3# x1 = x2 >> x3,逻辑右移,将寄存器x2的值右移 x3位后存到x1srli x1, x2, c
sra x1, x2, x3# x1 = x2 >>> x3,算术右移,将寄存器x2的值算术右移 x3位后存到x1srai x1, x2, c
数据传输指令¶
lw x1, 16(x2)# x1 = Memory[x2 + 16],从内存地址(x2 + 16)处加载一个字(32位)数据到x1, offset 必须是常数,不能是寄存器中的数- lb
- lbu
sw x1, 16(x2)# Memory[x2 + 16] = x1,将寄存器x1的值存储到内存地址(x2 + 16)处mv x1, x2# x1 = x2,数据移动,本质是将x2的值赋给x1
条件跳转指令¶
beq x1, x2, label# 如果x1等于x2,则跳转到label处执行bne x1, x2, label# 如果x1不等于x2,则跳转到label处执行blt x1, x2, label# 如果x1小于x2,则跳转到label处执行bge x1, x2, label# 如果 x1 大于等于 x2,则跳转到label处执行